17 May, 2023
9 Effective Sales Commission Structures: Industry-Specific Examples and Insights
Sales Commission
•
Written by McAlign
Introduction
An organisation's sales commission structure determines how its salespeople are compensated. Although it is a complicated and confusing topic, it is very important for you to understand how you are paid as well as how much you can expect to earn in the future.
There are many types of commission structures, each with its own pros and cons based on your industry, business model, and growth goals. We'll examine nine different commission structures by industry type: retail, B2B (business-to-business), travel & hospitality, technology/software, manufacturing, healthcare/medical device/pharma, financial services, real estate & construction.
A. Definition of Sales Commission Structures
The commission structure is the compensation plan that determines how sales representatives are compensated.
It consists of various payment models, such as a fixed percentage of revenue generated, tiered commissions based on performance, and bonuses.
B. Overview of the blog content
The purpose of this blog is to provide a deeper understanding of sales commission structures and their importance as motivators for sales teams.
We will discuss the different types of sales commission structures, their formulas, and examples.
We will also discuss sales commission structures by industry and title, highlighting each industry's unique characteristics.
Last but not least, we will address frequently asked questions and provide a conclusion to assist businesses in selecting the most appropriate commission structure for their sales teams.
Understanding Sales Commission Structures
An organisation's sales commission structure plays a critical role in motivating its sales teams. By understanding how these structures work, what factors influence them, and their benefits, you can develop more effective sales strategies. The purpose of this article is to explore the concept of sales commission, the factors that influence it, and the benefits of implementing effective commission structures.
A. The Concept of Sales Commission
A sales commission is an incentive-based compensation that companies offer to their sales representatives in order to motivate them to sell more. Typically, this type of compensation is based on the percentage of sales made by the salesperson. The primary objective of sales commission structures is to create a competitive environment that motivates high sales performance and rewards top performers.
B. Factors Affecting Commission Structures
Company size and industry: An organisation's size as well as its industry can have a significant impact on its commission structure. For example, large corporations with substantial resources may offer higher commission rates than smaller businesses or companies in highly competitive fields.
Sales cycle length: A longer sales cycle usually involves more complex sales processes and requires more effort on the part of sales representatives. Due to this, companies might design commission structures to reward sales representatives for closing deals with longer sales cycles, usually through a higher commission rate.
Sales targets and quotas: Creating an effective commission structure requires setting clear sales targets and quotas. By setting benchmarks for rewarding sales representatives, tiered commission structures can be created that incentivize higher performance.
Employee experience and expertise: In comparison to their less experienced counterparts, more experienced and skilled sales representatives might have higher commission rates. The difference in commission rates is a recognition of the experience, knowledge, and connections that veteran salespeople bring to the table.
C. Benefits of Effective Commission Structures
Increased motivation: Sales representatives who are motivated by a well-designed commission structure are more likely to close deals and exceed their targets.
Higher employee retention: By rewarding hard work and dedication, competitive commission structures can help retain top-performing sales representatives. Companies offering attractive commission structures will also be able to attract new talent, as prospective employees will be attracted to them.
Enhanced sales performance: Commission structures that motivate sales representatives to work harder and smarter can lead to increased sales performance and, ultimately, higher revenues.
Clear performance metrics: Measurable performance metrics allow management to evaluate sales representatives' performance in a transparent and objective manner, allowing them to identify and address any weaknesses.

The Importance of Sales Commission Structures
For a company to succeed, a well-constructed sales commission structure is essential. Besides motivating sales teams, it also promotes growth, increases sales, and retains top talent. The purpose of this section is to provide a comprehensive overview of the importance of sales commission structures.
A. Motivating Sales Teams
Incentives drive performance: For reaching or exceeding sales targets, sales representatives are rewarded with commission structures. Having a connection between performance and compensation can motivate sales teams to work harder.
Healthy competition: As sales representatives compete to earn higher commissions, commission structures can foster a competitive environment. As a result of this friendly rivalry, both employers and employees can benefit from increased productivity.
B. Encouraging Growth and Increasing Sales
Aligning goals: A sales commission structure aligns the goals of sales representatives with the overarching objectives of the company. By incentivizing sales teams to close deals and generate revenue, they become more focused on driving growth.
Adapting to market changes: Adapting commission structures to market changes allows companies to focus sales teams on products or services that are in high demand or have higher profit margins. When market conditions are challenging, businesses can still be competitive and maintain growth through this adaptability.
C. Retaining Top Talent
Rewarding excellence: Top-performing sales representatives are recognized and rewarded for their hard work and dedication through a well-designed commission structure. A sense of loyalty and job satisfaction is fostered by this recognition, in addition to motivating employees to keep performing at their best.
Attracting new talent: It is important for companies to offer competitive commission structures in order to attract new sales talent, since potential employees will be drawn to organisations that value their sales teams and provide ample opportunities for financial success.
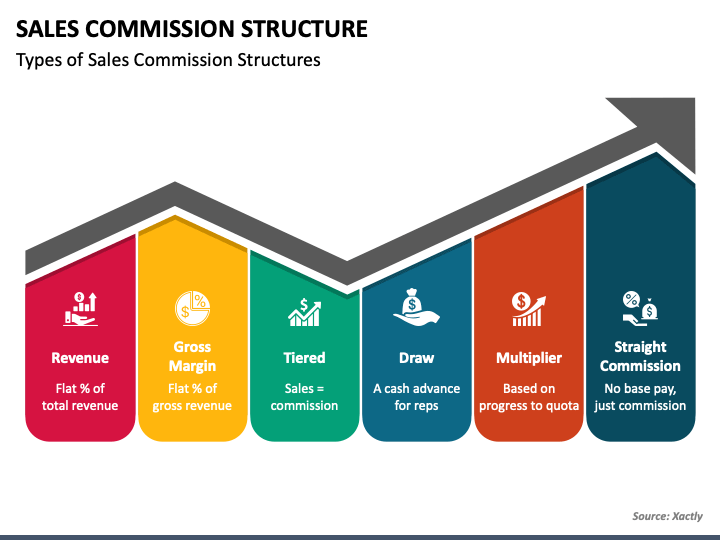
Types of Sales Commission Structures
A. Straight Commission Structure
Definition: Straight commissions are paid to sales representatives based on the revenue they generate from their sales, without any base salary or additional incentives.
Formula: Commission = Sales Revenue × Commission Rate
Examples: A sales representative sells a product worth $10,000 with a 10% commission rate. Their commission would be $1,000 (10,000 × 0.10).
B. Tiered Commission Structure
Definition: Tiered commission structures pay sales representatives varying commission rates based on their sales achievements, with higher commission rates for higher sales.
Formula: Commission = Tiered Commission Rate × Sales Revenue
Examples: A sales representative earns a 5% commission on sales up to $5,000, 10% on sales between $5,001 and $10,000, and 15% on sales above $10,000. If they sell $12,000 worth of products, their commission would be $1,450 [(5,000 × 0.05) + (5,000 × 0.10) + (2,000 × 0.15)].
C. Profit-Based Commission Structure
Definition: Profit-based commissions pay sales representatives a percentage of the profit generated from their sales rather than the total revenue they generate.
Formula: Commission = Sales Profit × Commission Rate
Examples: A sales representative sells a product for $10,000 with a 40% profit margin and a 10% commission rate. Their commission would be $400 [(10,000 × 0.40) × 0.10].
D. Draw Against Commission Structure
Definition: Draw against commission structures provide sales representatives with a base salary (draw) that must be repaid through earned commissions. Any commissions earned beyond the draw amount are kept by the sales representative.
Formula: Commission = (Total Commissions Earned - Draw Amount) if Total Commissions Earned > Draw Amount
Examples: A sales representative has a $2,000 monthly draw and earns $3,000 in commission for the month. They would keep $1,000 in commission after repaying the draw amount.
E. Territory Volume Commission Structure
Definition: Territory volume commission structures pay sales representatives based on total sales generated within their designated territory, regardless of individual performance.
Formula: Commission = Territory Sales Revenue × Commission Rate
Examples: A sales representative's territory generates $100,000 in sales revenue with a 3% commission rate. Their commission would be $3,000 (100,000 × 0.03).
F. Gross Margin Commission Structure
Definition: Gross margin commission structure pays sales representatives a percentage of the gross margin (sales revenue minus cost of goods sold) generated by their sales.
Formula: Commission = Gross Margin × Commission Rate
Examples: A sales representative sells a product for $10,000 with a cost of goods sold of $6,000 and a 10% commission rate. Their commission would be $400 [(10,000 - 6,000) × 0.10].
G. Unit Commission Structure
Definition: Unit commission structure pays sales representatives a fixed amount for each unit of a product or service sold.
Formula: Commission = Units Sold × Commission Rate per Unit
Examples: A sales representative sells 50 units of a product with a $20 commission per unit. Their commission would be $1,000 (50 × 20).
H. Bonus Commission Structure
Definition: Bonus commission structures offer sales representatives additional money for achieving specific goals, milestones, or targets.
Formula: Commission = Regular Commission + Bonus
Examples: A sales representative earns a $2,500 regular commission and achieves a sales target that qualifies them for a $500 bonus. Their total commission would be $3,000 (2,500 + 500).
Picture Source: Xactly
Sales Commission Structures by Industry and Titles
A. Real Estate Industry
Common commission structures: The commission structure for real estate agents typically involves a percentage of the sale price paid as commission. A split commission structure between buying and selling agents is also common.
Formulas and examples: A real estate agent sells a property for $300,000 with a 6% commission rate. Their commission would be $18,000 (300,000 × 0.06)
B. Retail Industry
Common commission structures: The commission structure for retail sales associates typically consists of a base salary plus a commission based on unit sales, revenue, or profit margin.
Formulas and examples: A retail sales associate earns a $10 commission per unit sold and sells 20 units in a month. Their commission would be $200 (10 × 20).
C. Automotive Industry
Common commission structures: A car sales professional typically works on a base salary plus commission, with commissions calculated based on the gross profit margin or a fixed amount.
Formulas and examples: A car salesperson sells a car for $25,000 with a $2,000 gross profit margin and a 20% commission rate. Their commission would be $400 (2,000 × 0.20).
D. Insurance Industry
Common commission structures:
The compensation structure of insurance agents is often a straight commission structure or a combination of a base salary and a commission structure. Most insurance agents work on a commission-only basis or combine their salary with commissions
Formulas and examples: An insurance agent sells a policy with a $1,000 annual premium and a 10% commission rate. Their commission would be $100 (1,000 × 0.10).
E. Technology Industry
Common commission structures: The compensation structure of insurance agents is often a straight commission structure or a combination of a base salary and a commission structure, commissions being based on total sales revenue or a tiered commission structure.
Formulas and examples: A technology sales representative earns a 5% commission on sales up to $10,000 and 10% on sales above $10,000. If they sell $15,000 worth of products, their commission would be $1,000 [(10,000 × 0.05) + (5,000 × 0.10)].
F. Healthcare Industry
Common commission structures: The compensation structure of insurance agents is often a straight commission structure or a combination of a base salary and a commission structure on total sales revenue, units sold, or a tiered commission structure.
Formulas and examples: A medical sales representative earns a $50 commission per unit sold and sells 30 units in a month. Their commission would be $1,500 (50 × 30).
G. Financial Services Industry
Common commission structures: The compensation structure of insurance agents is often a straight commission structure or a combination of a base salary and a commission structure calculated as a percentage of assets under management, transaction value, or as a fixed fee per transaction
Formulas and examples: A financial advisor manages a portfolio worth $1 million and charges a 1% annual management fee. Their commission would be $10,000 (1,000,000 × 0.01).
H. Hospitality Industry
Common commission structures: The compensation structure of insurance agents is often a straight commission structure or a combination of a base salary and a commission structure with commissions being based on room nights sold, event bookings, or total sales revenue.
Formulas and examples: A hotel sales representative earns a 5% commission on event bookings and books an event worth $20,000. Their commission would be $1,000 (20,000 × 0.05).
I. Manufacturing Industry
Common commission structures: The compensation structure of insurance agents is often a straight commission structure or a combination of a base salary and a commission structure, commissions being based on total sales revenue, units sold, or a tiered commission structure.
Formulas and examples: A manufacturing sales representative earns a 3% commission on sales up to $50,000 and 5% on sales above $50,000. If they sell $60,000 worth of products, their commission would be $2,500 [(50,000 × 0.03) + (10,000 × 0.05)].
J. Telecommunications Industry
Common commission structures: The compensation structure of insurance agents is often a straight commission structure or a combination of a base salary and a commission structure, with commissions being based on total sales revenue, new customer acquisitions, or a tiered commission structure.
Formulas and examples: A telecommunications sales representative earns a 10% commission on new customer acquisitions and acquires 15 new customers with an average contract value of $1,200. Their commission would be $1,800 (15 × 1,200 × 0.10).
K. Advertising Industry
Common commission structures: The compensation structure of insurance agents is often a straight commission structure or a combination of a base salary and a commission structure, with commissions being calculated as a percentage of the advertising revenue generated or a fixed amount per advertising sale.
Formulas and examples: An advertising sales representative earns a 15% commission on total advertising revenue they generate and closes $40,000 worth of advertising deals. Their commission would be $6,000 (40,000 × 0.15).
L. Professional Services Industry
Common commission structures: The compensation structure of insurance agents is often a straight commission structure or a combination of a base salary and a commission structure, with commissions being based on total sales revenue, new client acquisitions, or a tiered commission structure.
Formulas and examples: A professional services sales representative earns a $500 commission per new client acquired and signs 10 new clients in a month. Their commission would be $5,000 (500 × 10).
M. Renewable Energy Industry
Common commission structures: The compensation structure of insurance agents is often a straight commission structure or a combination of a base salary and a commission structure with commissions being based on total sales revenue, installations, or a tiered commission structure.
Formulas and examples: A renewable energy sales representative earns a 7% commission on sales up to $100,000 and 10% on sales above $100,000. If they sell $120,000 worth of products, their commission would be $9,400 [(100,000 × 0.07) + (20,000 × 0.10)].
Conclusion
A. Importance of finding the right commission structure
Finding the right commission structure is crucial for the success of your sales team and the growth of your business. A well-designed commission structure can help attract top talent, motivate sales representatives to perform at their best, and drive revenue growth.
B. Encouragement to review and adjust commission structures as needed
As your business evolves, it's essential to review and adjust your commission structures as needed. Regularly evaluating the effectiveness of your commission structure and making adjustments based on your sales team's performance, market conditions, and company goals can help ensure that your sales compensation plan remains competitive and effective in driving sales success.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. What is a sales commission structure?
Commission structures reward sales representatives based on their performance in generating sales revenue and meeting sales targets. They typically include base salaries, commissions, and/or bonuses.
B. How does a sales commission structure work?
A sales commission structure works by setting specific targets or goals for sales representatives to achieve, and then compensating them based on their success in achieving those targets or goals. Commissions can be calculated by calculating a percentage of total sales revenue generated, a fixed amount per sale, or by using a tiered system where commission rates increase as sales targets are reached.
C. How can I choose the right commission structure for my business?
To choose the right commission structure for your business, consider the following factors:
Industry norms: Research the common commission structures used in your industry, as this can provide valuable insights into what works best for your specific market.
Sales cycle: Evaluate the length and complexity of your sales cycle, as this can impact the effectiveness of different commission structures.
Goals and objectives: Determine your company's sales goals and objectives, and choose a commission structure that aligns with those targets.
Employee motivation: Consider what type of commission structure is most likely to motivate your sales representatives, as this can impact their overall performance and job satisfaction.
Profit margins: Analyse your profit margins and ensure that the commission structure you choose is sustainable and does not negatively impact your bottom line.